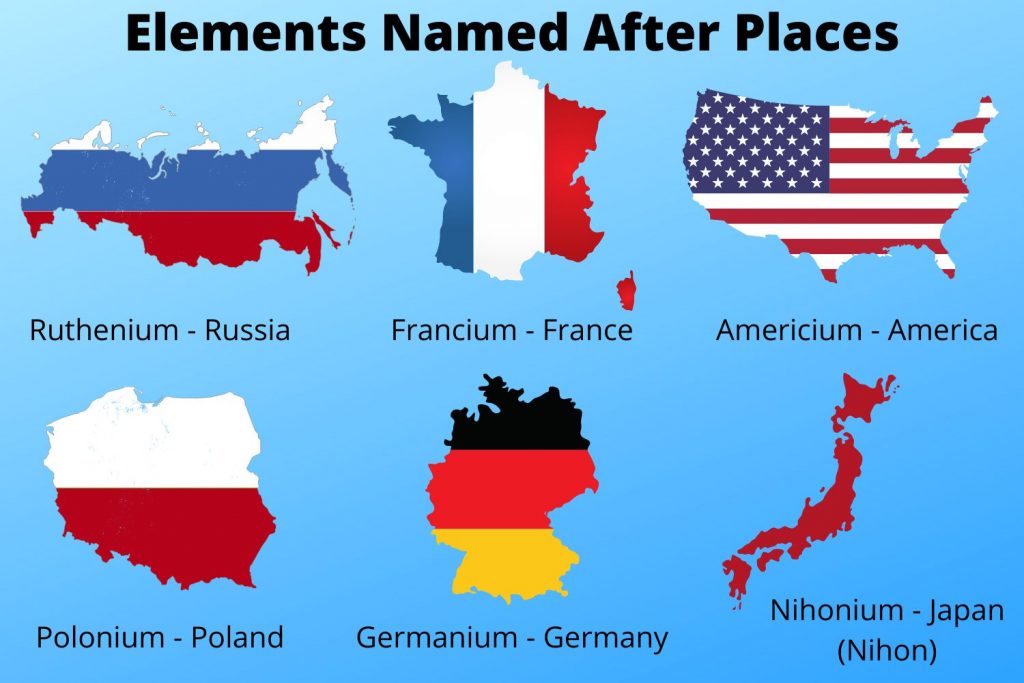
Discover The Element Named After A Continent
There is one element named after a continent: americium. Americium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a member of the actinide series, and is the heaviest element that can be found naturally in significant quantities (although trace amounts of elements with higher atomic numbers have been detected in uranium ores). Americium was first synthesized in 1944 by a team of scientists led by Glenn Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley.
Americium has a wide range of applications, including its use in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging. It is also used in the production of plutonium-238, which is used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to provide power for spacecraft and other remote applications. Americium's most common isotope, americium-241, has a half-life of 432.2 years. Americium is a relatively rare element, with an abundance in the Earth's crust of about 0.00005 parts per million.
Americium is named after the Americas, where it was first synthesized. The name was chosen to reflect the element's unique properties and its potential for use in a variety of applications.
One Element Named After a Continent
Americium is the only element named after a continent. It is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. Americium was first synthesized in 1944 by a team of scientists led by Glenn Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley.
- Discovery: Americium was discovered in 1944.
- Name: Americium is named after the Americas.
- Symbol: The symbol for americium is Am.
- Atomic number: Americium has an atomic number of 95.
- Radioactive: Americium is a radioactive element.
- Applications: Americium is used in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging.
- Half-life: Americium-241, the most common isotope of americium, has a half-life of 432.2 years.
- Abundance: Americium is a relatively rare element, with an abundance in the Earth's crust of about 0.00005 parts per million.
- Toxicity: Americium is a toxic element and can cause a variety of health problems, including cancer.
- Future: Americium has the potential to be used in a variety of future applications, including nuclear power and space exploration.
Americium is a versatile element with a wide range of applications. It is also a relatively rare element, which makes it valuable for certain applications. Americium is likely to continue to play an important role in a variety of fields in the future.
Discovery
The discovery of americium in 1944 was a significant event in the history of science. Americium is the only element named after a continent, and its discovery helped to pave the way for the development of new technologies and applications.
Americium was discovered by a team of scientists led by Glenn Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley. The team was bombarding plutonium with neutrons in a cyclotron when they produced americium. Americium is a radioactive element, and it was the first transuranium element to be discovered. Transuranium elements are elements that have an atomic number greater than 92, the atomic number of uranium.
The discovery of americium was important because it showed that it was possible to create new elements in the laboratory. This discovery led to the development of new technologies, such as nuclear power and nuclear medicine. Americium is used in a variety of applications, including smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging.
The discovery of americium also had a significant impact on our understanding of the periodic table. Americium is a member of the actinide series, which is a group of elements that are characterized by their high atomic numbers and their radioactive properties. The discovery of americium helped to complete the periodic table and to better understand the properties of the actinide series.
The discovery of americium was a major scientific achievement that has had a significant impact on our world. Americium is a versatile element with a wide range of applications, and it is likely to continue to play an important role in the future.
Name
The connection between "Name: Americium is named after the Americas" and "one element named after a continent" is significant. Americium is the only element named after a continent, and this reflects its unique properties and its potential for use in a variety of applications.
Americium was discovered in 1944 by a team of scientists led by Glenn Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley. The team was bombarding plutonium with neutrons in a cyclotron when they produced americium. Americium is a radioactive element, and it was the first transuranium element to be discovered. Transuranium elements are elements that have an atomic number greater than 92, the atomic number of uranium.
The name "americium" was chosen to reflect the element's unique properties and its potential for use in a variety of applications. Americium is a versatile element with a wide range of applications, including its use in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging. It is also used in the production of plutonium-238, which is used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to provide power for spacecraft and other remote applications.
The fact that americium is named after the Americas is a reminder of the important role that the Americas have played in the development of science and technology. The discovery of americium was a major scientific achievement, and it has had a significant impact on our world. Americium is a valuable element with a wide range of applications, and it is likely to continue to play an important role in the future.
Symbol
The symbol for americium is Am, which is derived from the element's name. The symbol is used to represent americium in chemical formulas and equations. It is also used to identify americium in various applications, such as in the labeling of radioactive materials.
- Unique identification: The symbol Am uniquely identifies americium and distinguishes it from all other elements. It is used to represent americium in the periodic table and in chemical reactions.
- Chemical formulas: The symbol Am is used in chemical formulas to represent americium atoms. For example, the chemical formula for americium dioxide is AmO2.
- Nuclear reactions: The symbol Am is used in nuclear reactions to represent americium atoms. For example, the following nuclear reaction represents the production of americium-241 from plutonium-241:
The symbol Am is an important tool for scientists and engineers who work with americium. It is used to identify americium in various applications and to represent americium in chemical formulas and nuclear reactions.
Atomic number
The atomic number of americium is 95, which means that it has 95 protons in its nucleus. This places americium in the actinide series of elements, which are characterized by their high atomic numbers and their radioactive properties.
- Unique identity: The atomic number of an element is what defines its identity. Americium's atomic number of 95 means that it is unique among all other elements.
- Position in the periodic table: The atomic number of an element determines its position in the periodic table. Americium's atomic number of 95 places it in the actinide series, between plutonium and curium.
- Chemical properties: The atomic number of an element influences its chemical properties. Americium's atomic number of 95 gives it a variety of interesting and useful chemical properties.
- Nuclear properties: The atomic number of an element also influences its nuclear properties. Americium's atomic number of 95 makes it a radioactive element with a relatively long half-life.
The atomic number of americium is a fundamental property that has a significant impact on its identity, its position in the periodic table, its chemical properties, and its nuclear properties. Americium's atomic number of 95 makes it a unique and valuable element with a wide range of applications.
Radioactive
Americium is a radioactive element, meaning that its atoms have unstable nuclei that decay over time, emitting radiation. This radioactivity is a fundamental property of americium that has a significant impact on its identity and its applications.
Americium's radioactivity is due to the fact that its atomic nuclei have too many neutrons. In order to achieve a more stable configuration, americium nuclei decay by emitting alpha particles, which are helium nuclei. This process of radioactive decay is what gives americium its characteristic radioactivity.
The radioactivity of americium is important because it allows americium to be used in a variety of applications. For example, americium is used in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging. In smoke detectors, americium-241 is used to ionize the air, which allows the detector to detect the presence of smoke particles. In neutron sources, americium-241 is used to produce neutrons, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as cancer treatment and materials analysis. In medical imaging, americium-241 is used to produce gamma rays, which can be used to create images of the inside of the body.
The radioactivity of americium also has some challenges. Americium is a toxic substance, and it can be harmful to human health if it is not handled properly. Americium is also a radioactive waste product, and it must be disposed of properly in order to protect the environment.
Overall, the radioactivity of americium is a fundamental property that has a significant impact on its identity and its applications. Americium's radioactivity allows it to be used in a variety of important applications, but it also presents some challenges that must be carefully managed.
Applications
Americium's unique properties make it a valuable element for a variety of applications. Its radioactivity allows it to be used in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging.
- Smoke detectors: Americium-241 is used in smoke detectors to ionize the air, which allows the detector to detect the presence of smoke particles. Smoke detectors are an important safety device that can help to save lives by alerting people to the presence of a fire.
- Neutron sources: Americium-241 is used in neutron sources to produce neutrons, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as cancer treatment and materials analysis. Neutron sources are used in a variety of applications, including cancer treatment, materials analysis, and nuclear research.
- Medical imaging: Americium-241 is used to produce gamma rays, which can be used to create images of the inside of the body. Medical imaging is an important diagnostic tool that can help doctors to identify and treat a variety of medical conditions.
Americium's applications are diverse and important. Its unique properties make it a valuable element for a variety of applications, including safety, medical, and scientific research.
Half-life
The connection between americium's half-life and its status as the only element named after a continent lies in the element's unique properties and its potential for use in various applications. Americium-241's relatively long half-life contributes to its stability and makes it suitable for various applications where long-term radioactivity is required.
Americium-241's half-life enables its use in smoke detectors, a crucial safety device in homes and buildings. In smoke detectors, americium-241 ionizes the air, allowing for the detection of smoke particles. Its long half-life ensures the continuous functioning of smoke detectors over an extended period without the need for frequent replacement of the radioactive source.
In medical applications, americium-241 finds use in portable X-ray devices and cancer treatment. Its long half-life provides a reliable source of radiation for these applications. Americium-241's ability to emit alpha particles makes it suitable for targeted alpha therapy, a form of cancer treatment that involves the use of alpha-emitting isotopes to target and destroy cancer cells.
Understanding the half-life of americium-241 is crucial for its safe handling and disposal. Its relatively long half-life requires careful management of americium-containing materials throughout their life cycle, from production to disposal. Proper storage and disposal techniques are necessary to minimize the potential for environmental contamination and ensure public safety.
In summary, the half-life of americium-241, the most common isotope of americium, is a key factor that contributes to its unique properties and its suitability for various applications. Its stability and long-term effectiveness make americium-241 valuable in fields such as smoke detection, medical imaging, and cancer treatment. Understanding the half-life of americium-241 is essential for its responsible use and management throughout its lifecycle.
Abundance
Americium's scarcity, despite being the only element named after a continent, highlights its unique nature and the remarkable circumstances that led to its discovery and subsequent applications.
- Rarity and Value: Americium's low abundance makes it a valuable resource, particularly for specialized applications where its unique properties are crucial. Its rarity contributes to its significance in scientific research, medical treatments, and industrial processes.
- Geological Processes: The scarcity of americium in the Earth's crust is attributed to its formation through nuclear reactions involving uranium and plutonium. These reactions occur naturally but are rare, resulting in the limited availability of americium.
- Half-life and Decay: Americium's radioactive nature and relatively long half-life of 432.2 years further contribute to its scarcity. As americium decays over time, its abundance in the environment gradually decreases.
- Anthropogenic Sources: While americium occurs naturally, human activities, such as nuclear power generation and weapons production, have also contributed to its presence in the environment. These anthropogenic sources can increase the localized abundance of americium, but they do not significantly alter its overall scarcity.
Americium's rarity, coupled with its unique properties, makes it an element of great interest and value. Its scarcity necessitates careful management and responsible use, ensuring its availability for future generations and applications.
Toxicity
Americium's status as the only element named after a continent highlights its unique nature, and its toxicity is an intrinsic property that demands attention. Understanding the toxic effects of americium is crucial for responsible handling and management, ensuring the safe utilization of this element while minimizing potential risks.
- Radiation Exposure and Health Risks: Americium's radioactivity poses significant health risks if proper precautions are not taken. Exposure to americium can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or contact with contaminated materials. Alpha particles emitted by americium can damage DNA and increase the risk of cancer, particularly bone cancer and leukemia.
- Environmental Impact: Americium's long half-life and potential for environmental contamination raise concerns about its impact on ecosystems. Improper disposal or accidental releases can lead to the accumulation of americium in soil, water, and living organisms, posing risks to wildlife and potentially entering the human food chain.
- Occupational Hazards: Workers in nuclear facilities, research laboratories, and industries that utilize americium must adhere to strict safety protocols to minimize exposure. Proper handling, protective gear, and regular monitoring are essential to prevent internal contamination and its associated health risks.
- Regulatory Measures: Governments and regulatory bodies have established guidelines and regulations for the safe handling, storage, and disposal of americium. These measures aim to protect the public and the environment from potential exposure and contamination.
The toxicity of americium underscores the importance of responsible stewardship of this element. Striking a balance between its unique properties and potential risks requires a multi-faceted approach involving scientific research, technological advancements, and stringent regulatory frameworks. Continued efforts in these areas will ensure the safe utilization of americium while minimizing its potential adverse effects.
Future
The connection between "Future: Americium has the potential to be used in a variety of future applications, including nuclear power and space exploration" and "one element named after a continent" lies in the unique properties and potential of americium as the only element named after a continent. Americium's unique properties, including its radioactivity, long half-life, and ability to produce neutrons, make it a valuable resource for a variety of future applications, particularly in the fields of nuclear power and space exploration.
In nuclear power, americium can be used as a fuel source in nuclear reactors. Americium-241 is a fissile isotope that can be used to produce energy in nuclear power plants. Americium-242m is another isotope that can be used in nuclear batteries, which provide a long-lasting and reliable source of power for remote applications such as space probes and satellites.
In space exploration, americium is used as a power source for radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs), which convert heat from the decay of americium-241 into electricity. RTGs have been used to power spacecraft such as the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 probes, which have been exploring the outer planets of our solar system for decades. Americium-241 is also used in portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometers, which are used to analyze the composition of materials on the surface of Mars and other planets.
The practical significance of understanding the potential of americium for future applications is that it enables scientists and engineers to develop new technologies that can benefit humanity in a variety of ways. Nuclear power generated from americium can help to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and transition to a clean energy future. Space exploration powered by americium can help us to better understand our solar system and beyond, and potentially lead to new discoveries and advancements in science and technology.
FAQs on the Element Named After a Continent
Americium, the only element named after a continent, has unique properties and applications. Here are some frequently asked questions about americium:
Question 1: What is americium?
Americium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a member of the actinide series and is the heaviest element that can be found naturally in significant quantities.
Question 2: Why is americium named after a continent?
Americium was discovered in 1944 by a team of scientists led by Glenn Seaborg at the University of California, Berkeley. The team chose to name the element after the Americas, where it was first synthesized.
Question 3: What are the applications of americium?
Americium has a wide range of applications, including its use in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging. It is also used in the production of plutonium-238, which is used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to provide power for spacecraft and other remote applications.
Question 4: Is americium dangerous?
Yes, americium is a toxic element and can cause a variety of health problems, including cancer. Exposure to americium can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or contact with contaminated materials. Proper precautions must be taken when handling americium.
Question 5: What is the future of americium?
Americium has the potential to be used in a variety of future applications, including nuclear power and space exploration. Americium-241 can be used as a fuel source in nuclear reactors and in nuclear batteries. It is also used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to power spacecraft.
Summary: Americium is a unique and valuable element with a wide range of applications. It is important to understand the properties and applications of americium, as well as the potential risks associated with its use.
Transition to the next article section: Americium is just one of many fascinating elements that have been discovered by scientists. In the next section, we will explore the history of the periodic table and the role that scientists have played in unraveling the mysteries of the elements.
Tips Related to the Element Named After a Continent
Americium is the only element named after a continent, and its unique properties make it a valuable resource for a variety of applications. Here are some tips to help you better understand americium and its applications:
Tip 1: Understand the Significance of Americium's Name
Americium is named after the Americas, where it was first synthesized. This reflects the importance of the Americas in the development of science and technology.
Tip 2: Learn About Americium's Properties
Americium is a radioactive element with a relatively long half-life. It is a member of the actinide series and is the heaviest element that can be found naturally in significant quantities.
Tip 3: Explore Americium's Applications
Americium has a wide range of applications, including its use in smoke detectors, neutron sources, and medical imaging. It is also used in the production of plutonium-238, which is used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to provide power for spacecraft and other remote applications.
Tip 4: Be Aware of Americium's Toxicity
Americium is a toxic element and can cause a variety of health problems, including cancer. Proper precautions must be taken when handling americium.
Tip 5: Consider Americium's Future Potential
Americium has the potential to be used in a variety of future applications, including nuclear power and space exploration. Americium-241 can be used as a fuel source in nuclear reactors and in nuclear batteries. It is also used in radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) to power spacecraft.
Summary: Americium is a unique and valuable element with a wide range of applications. By understanding the properties, applications, and potential risks of americium, you can better appreciate its importance and its potential for future use.
Transition to the article's conclusion: Americium is just one of many fascinating elements that have been discovered by scientists. In the next section, we will explore the history of the periodic table and the role that scientists have played in unraveling the mysteries of the elements.
Conclusion
Americium, the only element named after a continent, is a fascinating and valuable resource with a wide range of applications. Its unique properties, including its radioactivity and long half-life, make it a promising candidate for future technologies in nuclear power and space exploration.
As we continue to explore the potential of americium and other elements, it is important to remember the importance of scientific research and responsible stewardship of our natural resources. By working together, we can harness the power of science to solve some of the world's most pressing challenges and build a better future for all.
Unveiling The Educational Journey Of Laura Ingraham: Insights And Revelations
Unveiling The Secrets Of Indonesian Nationality: Discoveries And Insights Await
Unveiling The Multifaceted World Of "Zac Goldsmith, The Agency Wife"

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/element-list-names-atomic-numbers-606529_V1_FINAL-f332cfc84a494b7782d84fc986cdaf86.png)
ncG1vNJzZmiooqTDsL%2FTcWWapaNoe6W1xqKrmqSfmLKiutKpmJydo2OwsLmOqKWeZZWhsq6xza1kp5mdmrFurcWtnKtlkWKwsLrToqWepqRjtbW5yw%3D%3D